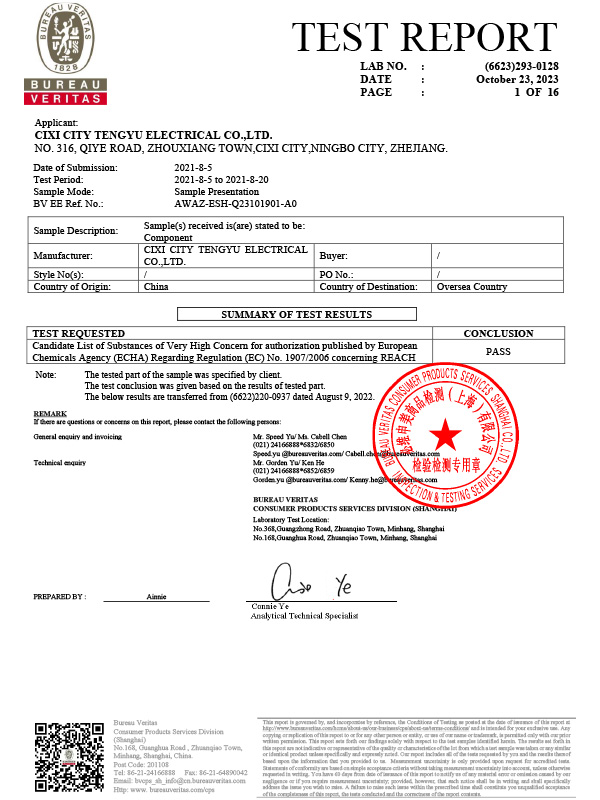
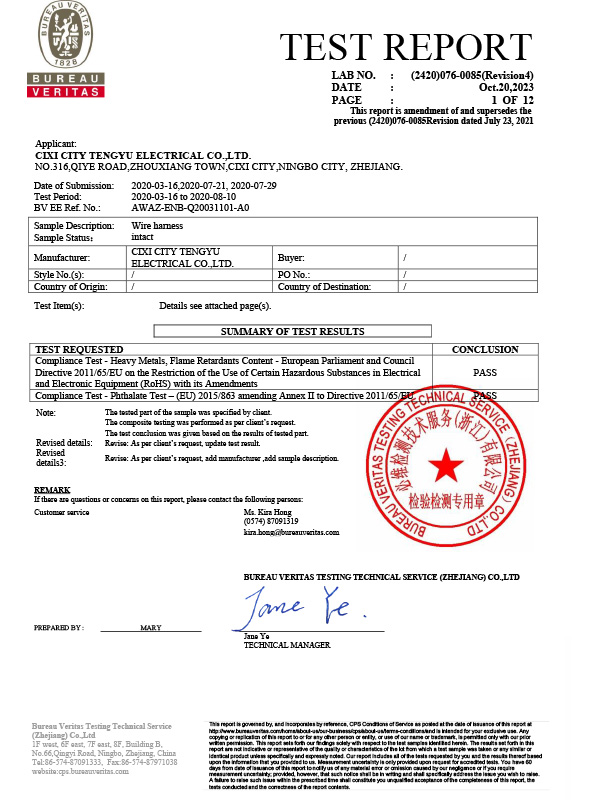
What are the commonly used materials for fan heater NTC temperature sensors?
Among modern household appliances, fan heaters are efficient and convenient heating devices. One of the core components of their temperature control systems is the NTC (negative temperature coefficient) temperature sensor. NTC temperature sensors are widely used for temperature control and safety protection in fan heaters due to their high sensitivity, fast response speed, and low cost.
The core of a fan heater NTC temperature sensor is the thermistor material, whose resistance changes inversely with temperature. Commonly used materials include metal oxide semiconductor ceramics and leaded packaging materials.
First, metal oxide semiconductor ceramics are the core material of NTC sensors. Common metal oxides include nickel oxide (NiO), cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄), manganese oxide (MnO₂), copper oxide (CuO), and small amounts of iron oxide (Fe₂O₃). These materials form a stable polycrystalline structure after high-temperature sintering, exhibiting a distinct negative temperature coefficient. Nickel oxide is one of the most commonly used materials due to its stable resistance variation over a wide temperature range, high sensitivity, and relatively low cost, making it well-suited for fan heater applications. Cobalt oxide and manganese oxide are typically added as dopants to optimize the B value (thermal sensitivity coefficient) and temperature linearity, thereby ensuring sensor accuracy and stability in both high and low temperature operating conditions.
Secondly, the fan heater NTC sensor's packaging and lead materials also significantly impact its performance. The ambient temperature of a fan heater can exceed 100°C during operation, so the sensor requires a high-temperature-resistant packaging material, such as glass, ceramic, or high-temperature epoxy resin. These materials effectively isolate the sensitive element from the effects of air and moisture, improving the sensor's long-term stability and reliability. Tinned or nickel-plated copper wire is typically used as lead wire, offering excellent conductivity and high-temperature resistance, while also facilitating soldering or plugging into the fan heater's control circuitry.
Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. fully considers the impact of material selection on performance during the development and manufacturing of its NTC temperature sensors. Leveraging over 20 years of industry experience, the company has mastered internationally advanced production technology and a strict quality management system. Tengyu Electrical implements meticulous management in the proportioning of ceramic thermistor materials, sintering temperature control, and lead packaging processes. By optimizing the doping ratio of nickel oxide, cobalt oxide, and manganese oxide, the company is able to precisely control the B value and resistance-temperature characteristics of the NTC sensor, resulting in high sensitivity, fast response, and long life in fan heater temperature control systems.
Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. also prioritizes the environmental adaptability of materials. Fan heaters may be exposed to high humidity, dust, and frequent on-off cycles in home use. The choice of NTC sensor material directly impacts product stability and safety. The company undergoes rigorous material screening and durability testing to ensure the sensor maintains excellent performance in long-term high-temperature and humid environments. This not only enhances the fan heater user experience but also significantly reduces after-sales maintenance costs.
What is the difference between fan heater NTC temperature sensors and PTC sensors in fan heaters?
In modern fan heater design, the temperature control system is central to ensuring safe, efficient, and comfortable operation. Temperature control systems typically rely on temperature sensors, with the most commonly used types being NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient). While both are used for temperature detection and control, there are significant differences in their operating principles, applications, and control strategies.
The core characteristic of fan heater NTC temperature sensors is that their resistance decreases as temperature increases. This negative temperature coefficient makes NTC sensors ideal for precise temperature measurement and feedback control. In fan heaters, NTC sensors typically work in conjunction with control circuitry to monitor the temperature of the heating element or air outlet in real time. When the temperature reaches the set point, the control system precisely adjusts the heating power based on the resistance signal provided by the NTC sensor, achieving stable temperature control. NTC sensors offer fast response and high sensitivity, enabling continuous and precise temperature adjustment, thereby improving the comfort and energy efficiency of fan heaters.
In contrast, PTC sensors exhibit a positive temperature coefficient, increasing their resistance as temperature rises. PTC sensors are often used for self-limiting heating or overheating protection. Their operating principle is that their resistance increases rapidly with temperature. When the temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the PTC sensor's resistance increases significantly, automatically limiting the current flowing through the heating element and preventing overheating. This characteristic makes PTC sensors more suitable for safety protection in fan heaters rather than for continuous, precise temperature measurement. PTC sensors are easy to install and durable, making them suitable for preventing dry heating or unexpected high temperatures.
In terms of application effectiveness, NTC and PTC sensors complement each other in fan heaters. NTC sensors provide high-precision temperature feedback for intelligent temperature control and energy-saving regulation, while PTC sensors emphasize safety, ensuring that the device automatically limits the temperature or cuts off the current under abnormal operating conditions to protect users and equipment. For manufacturers, a correct understanding of the functional positioning of both sensors can help optimize the temperature control design of fan heaters and achieve a balance between safety and comfort.
Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. fully utilizes the advantages of NTC and PTC sensors in the development of fan heaters. Leveraging over 20 years of industry experience, the company has established internationally advanced production processes and a strict quality management system. Tengyu Electrical implements meticulous management in the material selection, resistance design, and packaging process of NTC sensors, ensuring high sensitivity and stability in various temperature environments. Furthermore, in the application of PTC sensors, the company prioritizes high-temperature resistance, aging resistance, and rapid current limiting to ensure safe operation of fan heaters under high temperatures or abnormal operating conditions.
How does the installation location of a fan heater's NTC temperature sensor affect its temperature control accuracy?
The fan heater NTC temperature sensor operates on the principle that resistance is negatively correlated with temperature. The fan heater control system determines the air temperature or heating element temperature by measuring the change in sensor resistance, thereby adjusting power output. If the sensor is improperly installed, the temperature control system may not be able to detect temperature changes in a timely manner, resulting in delayed temperature control or increased error. This phenomenon manifests in the fan as localized overheating, insufficient heating, or significant temperature fluctuations, affecting comfort and safety.
Generally, the selection of the NTC sensor installation location requires consideration of the following factors: First, the air flow path. A fan delivers heated air to the outlet via a fan. If the sensor is located far from the airflow path, the measured temperature may be lower than the actual outlet temperature, causing delayed temperature control or overheating. Second, the heating element temperature. When the sensor is close to the heating element, it can quickly detect changes in element temperature and achieve a quick response. However, if it is too close, it may be affected by the localized high temperature, resulting in an overly high temperature and misjudgment by the control system. Third, environmental interference. Fan interference, heat conduction from the housing, or other heat sources near the sensor can affect measurement accuracy. Therefore, the installation location must avoid direct interference from external heat sources.
Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. systematically optimizes the installation location of NTC sensors during the development and production of fan heaters. Leveraging over 20 years of industry experience, combined with internationally advanced production technology and a scientific management system, the company conducted multiple simulations and field measurements to verify sensor placement. Teng Yu Electrical uses aerodynamic simulations and temperature response testing to ensure that the NTC sensor can quickly sense the heating element temperature and accurately reflect the air outlet temperature, achieving high-precision and stable temperature control.
In addition, the company strictly controls the installation method and mounting structure during sensor installation. A well-designed mounting bracket and thermal conductivity design prevent thermal conduction errors caused by direct contact between the sensor and the housing, while ensuring the sensor's stable position during long-term use, unaffected by vibration or fan vibration. Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. also pays special attention to matching the sensor with the control circuit. By optimizing the voltage divider circuit and ADC sampling accuracy, the temperature control system fully utilizes the sensor's fast response characteristics, further improving the fan heater's temperature control accuracy. From the perspective of user experience and product safety, the optimized NTC sensor installation location is significantly beneficial. By strategically placing the sensor, the fan heater achieves a more uniform air outlet temperature, responds quickly to temperature changes, and avoids false triggering of overheat protection. This not only improves heating efficiency and comfort, but also extends the lifespan of the fan heater's core components. Cixi Tengyu Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. fully considers this in product design, using precise calculations and repeated verification to provide customers with high-performance and reliable fan heaters.



 中文简体
中文简体